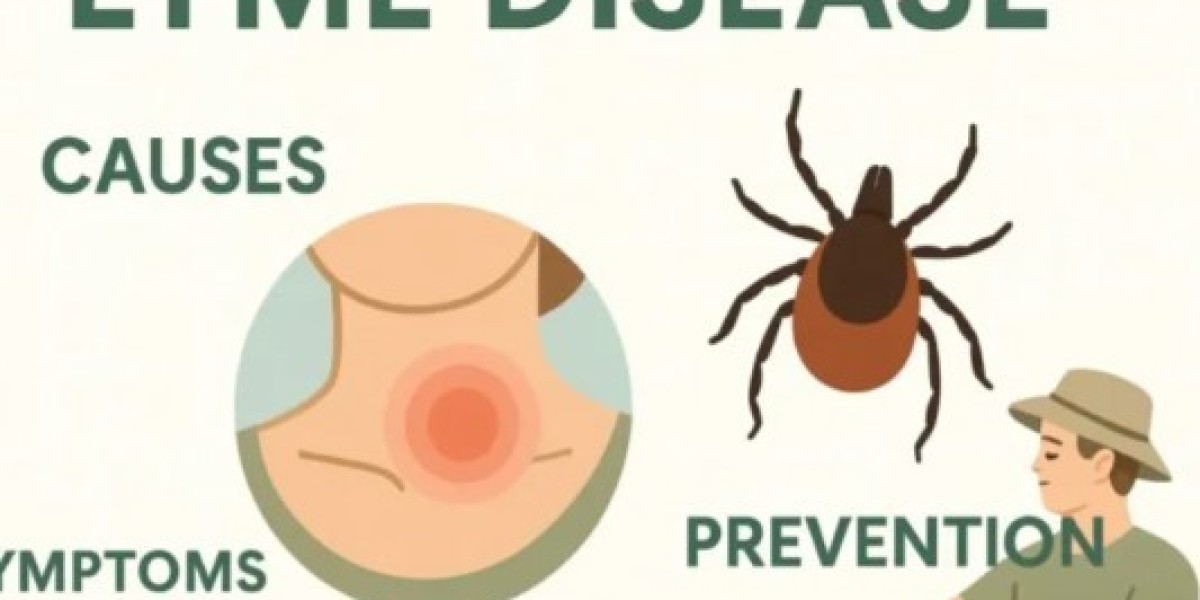
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection primarily
transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks (also called deer ticks). These tiny arachnids carry Borrelia bacteria, which enter the bloodstream during feeding. First identified in Lyme, Connecticut, in 1975, Lyme disease has since become the most common vector-borne illness in the Northern Hemisphere, with an estimated 476,000 diagnoses annually in the U.S. alone.
Symptoms: Recognizing the Stages
Lyme disease symptoms typically progress in stages and vary widely:
Early Localized Stage (3-30 days post-bite):
Erythema migrans (EM) rash: Expands gradually (often 5+ inches), sometimes resembling a “bull’s-eye” (though this pattern appears in only 20% of U.S. cases).
Flu-like symptoms: Fever, chills, headache, fatigue, muscle/joint aches, swollen lymph nodes.
Early Disseminated Stage (Weeks to months post-bite):
Additional EM rashes on other body parts.
Facial palsy (drooping on one/both sides).
Severe headaches, neck stiffness.
Heart palpitations (Lyme carditis).
Nerve pain, numbness, or tingling.
Late Disseminated Stage (Months to years post-bite):
Severe joint pain/swelling (Lyme arthritis), often in knees.
Neurological issues: Brain fog, memory problems, nerve damage.
In Europe: Skin swelling/discoloration (acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans).
Note: Not everyone develops the rash, and symptoms can overlap or occur without a known tick bite.
Lyme disease
Causes and Transmission
Pathogen: Borrelia burgdorferi (U.S.), B. afzelii or B. garinii (Europe/Asia).
Vector: Blacklegged ticks (Ixodes scapularis in Eastern U.S., I. pacificus in Western U.S., I. ricinus in Europe).
Transmission: Ticks must be attached 36-48 hours to transmit bacteria. Nymphs (poppy-seed-sized) cause most infections in spring/summer.
Risk Factors
Spending time in grassy/wooded areas (gardening, hiking, camping).
Living/traveling in endemic regions: Northeast, Mid-Atlantic, Upper Midwest U.S.; Europe, South Canada.
Pets that roam outdoors (can carry ticks indoors).